MIT 6.S081 Lecture 10: Multiprocessors and locking
Reading
- Read Locking
- read code

Locks introduction
-
apps wants to multiple cores
-
kernel must handle parallel sys calls
-
access shared data structure in parallel
-
-> locks for correct sharing
-
locks limit performance
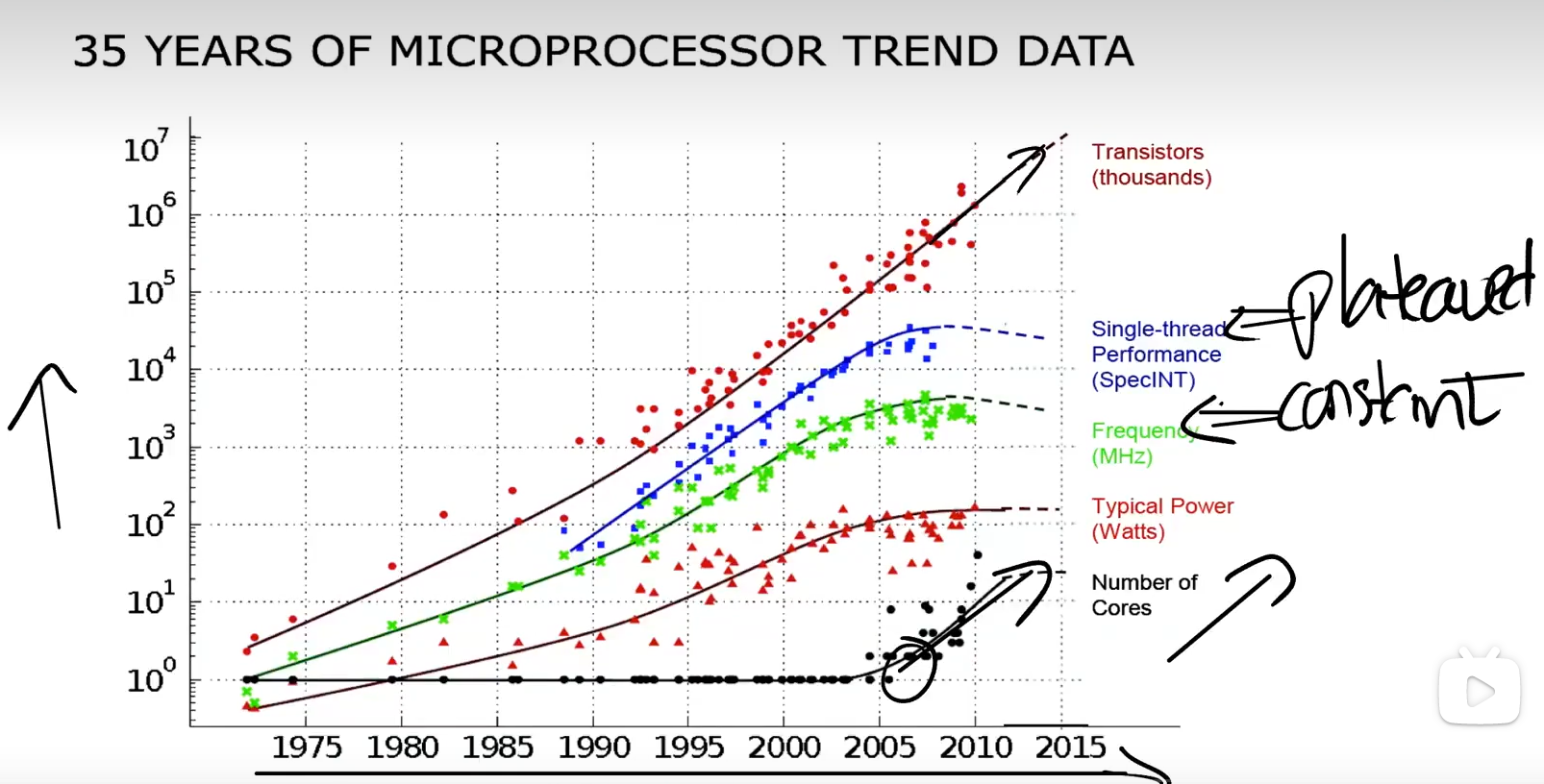
Microprocessor trend
Lock abstraction
-
struct lock
1 | // Mutual exclusion lock. |
1 | acquire(&l) |
-
程序有很多把锁,如果只有一把,串行影响性能,为达到某种程度的并行且保证正确性,程序使用多把锁
When to lock?
-
Constructive Rule: two process access a shared data structure + one is writing
-
too strict: lock free programming
-
too loose: printf(“xxxx”)
Could locking be automatic?
Lock perspective
-
avoid lost update
-
make multi-step operation atomatic
-
help maintain invariant
Dead lock
Locks vs modual
-
lock ordering -> global
-
锁使模块化变得困难
Locks vs performance
Implenment Lock
memory ordering
updating…
