MIT 6.S081 Lecture 9: Interrupts
Reading
- Read Chapter5
- read code

Interrupts
-
HW wants attention now, like keyboard and network device
-
系统调用,traps,interrupts都使用相同的处理模式
- save its work
- process interrupt
- resume its work
-
interrrupts的特殊之处
- asynchronous异步的
- concurrency between cpu and device
- program device
Where interrupts come from?
-
主板上的异步接口
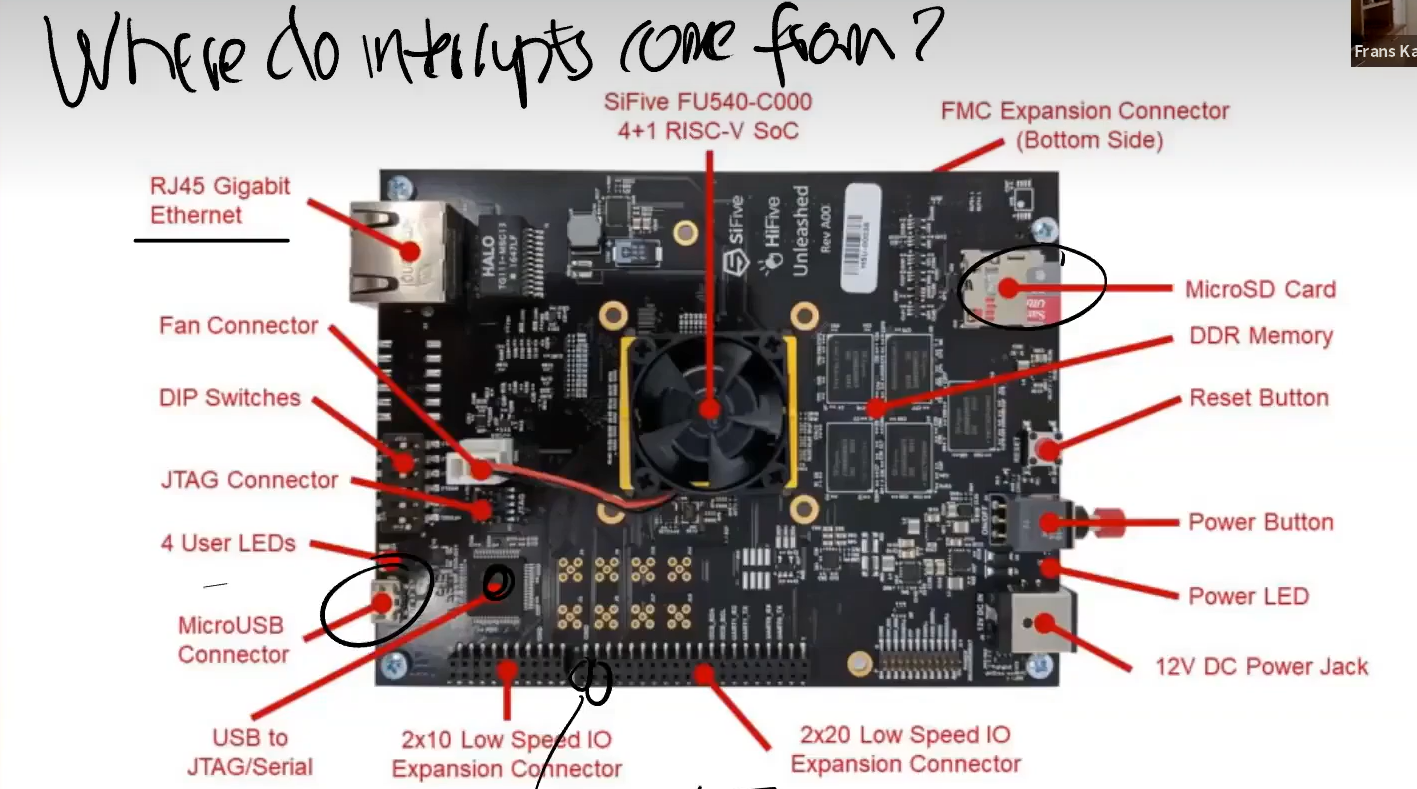
-
cpu架构
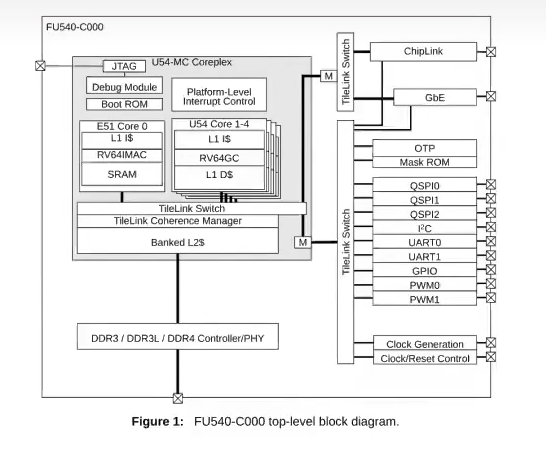
-
PLIC 平台级中断控制器
-
UART 通用异步收发器(Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter)
Driver manage device
-
经典的驱动架构
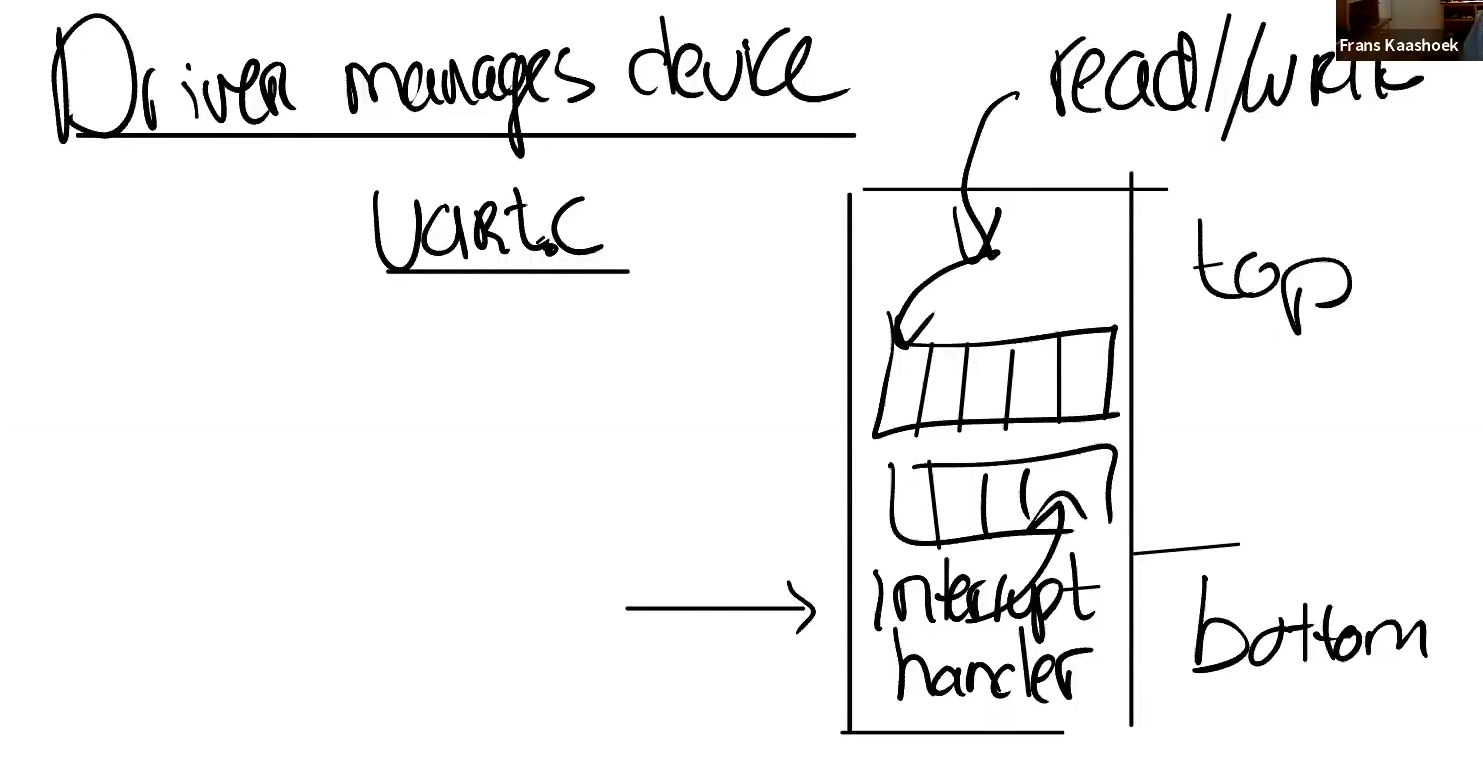
Programming Device
-
memory mapped I/O
-
ld/st read/write control register device
How does ‘$ ls’ work?
-
device puts ‘$’ into uart
-
uart generate interrupts when char has been sent
-
keyboard connect to generate interrupts
RISC-V support for interrupts
-
STE - one bit for E, S, T
-
SSTATE - bit enable/disable
-
SIP - interrrupt pending
-
SCAUSE
-
STVEC
Interrrupts and concurrency
-
device and cpu run in parallel
- producer / consumer parallelism
-
interrupts stops the current program
- user? OK
- kernel? 必要时设置取消interrupts来保证原子性
-
top of device and bottom of device run in parallel
- use locks
Interrupts evolution
-
polling(轮询)
- 对于高速设备节省,如高性能网卡
- 对于低速设备浪费性能,如键盘
-
interrupts(中断)
-
动态切换polling和interrupts
-
Tip: CS61C中关于设备访问的几种方式
- polling相当于到店排队问好了没,好了我拿走
- interrupts相当于准备好了通知你到店自取
- DMA相当于外卖送货上门,你去拿就行了
